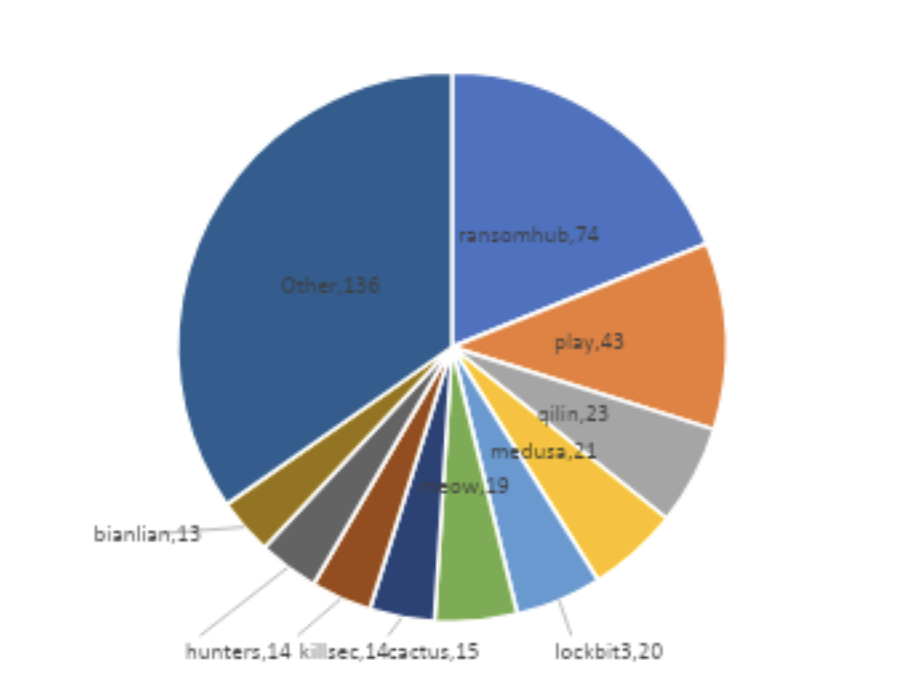
Ransomware is no longer just about locking up your data for ransom—it’s evolving fast and posing new, complex threats. Emerging groups like RansomHub are reshaping the landscape with fresh strategies, while familiar players like Lockbit see their influence wane. This shift toward data extortion, where sensitive data is stolen and held hostage, signals a new approach in ransomware tactics that affects sectors across the board, from manufacturing to healthcare and education.
RansomHub’s Rapid Rise
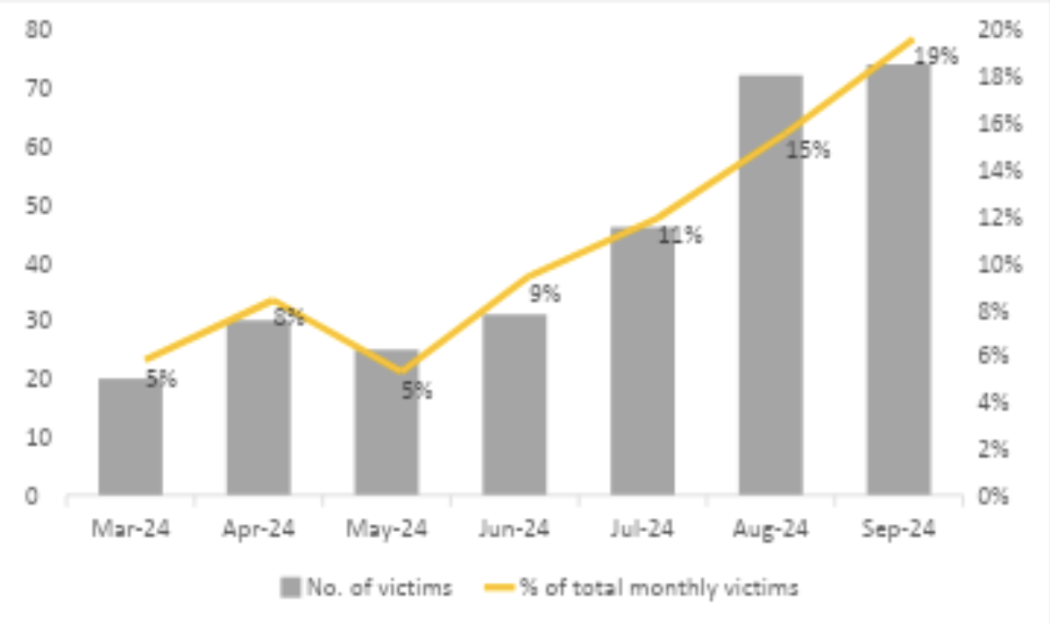
RansomHub, a newer player, quickly made its mark since early 2024. Unlike traditional ransomware attacks, this group’s RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) model allows affiliates to deploy sophisticated tools, notably remote encryption, which hides the attack better and makes it harder to prevent.
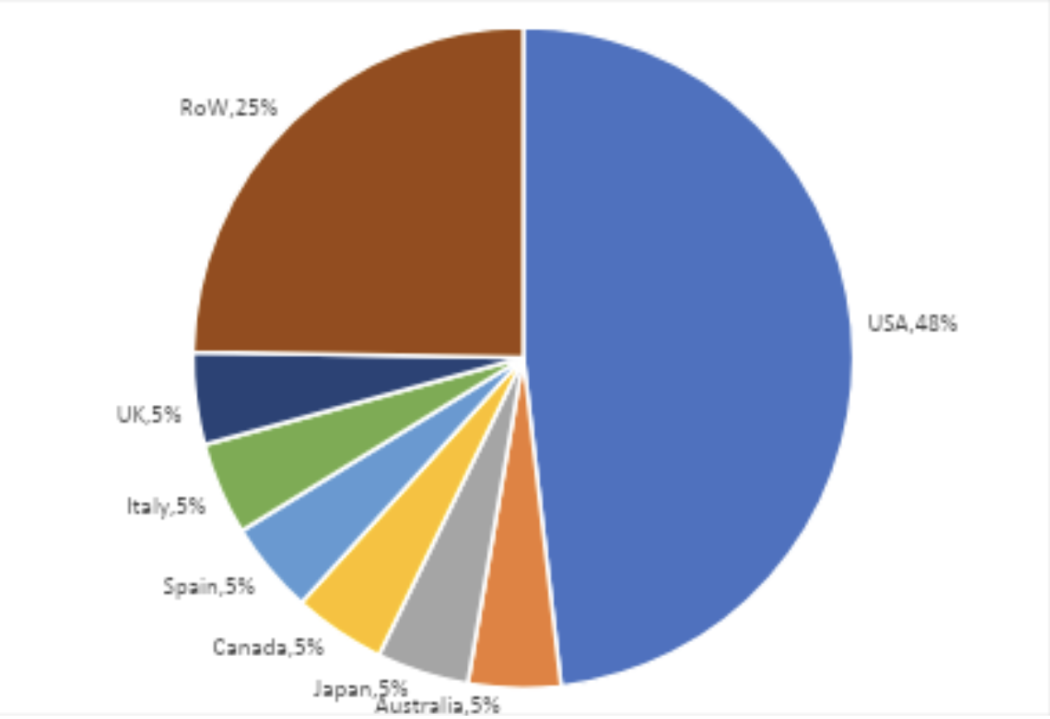
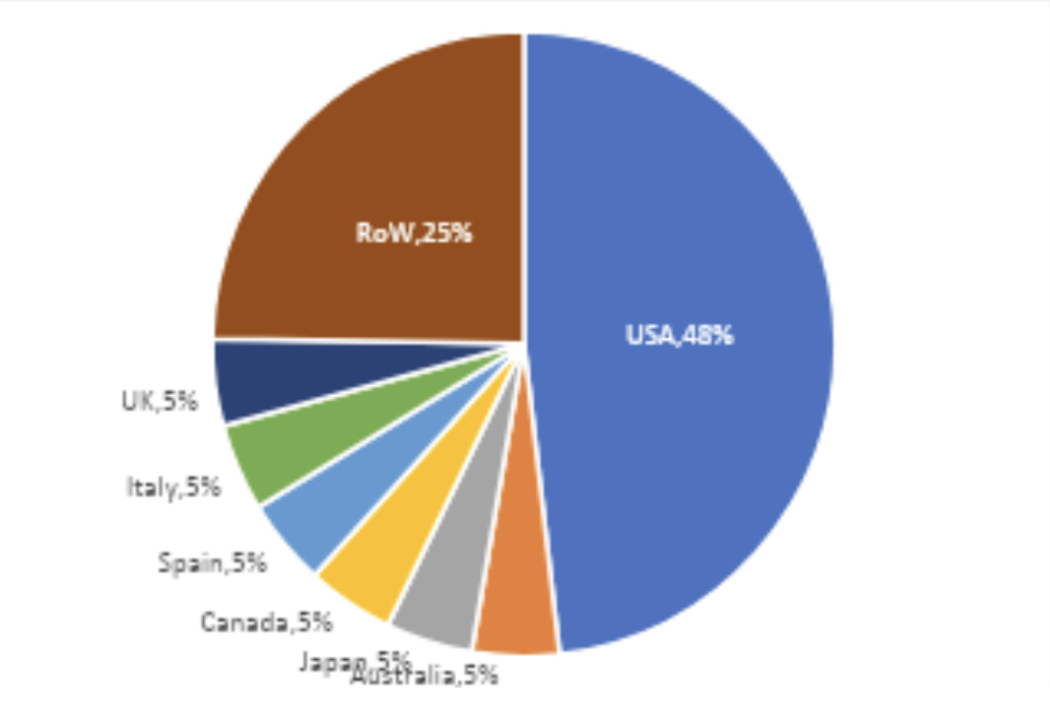
Key targets are U.S.-based companies in industrial manufacturing and healthcare, with 48% of RansomHub’s victims located in the U.S. Notably, even healthcare organizations, which RansomHub claimed to avoid, fell victim to attacks, showing that affiliates may have considerable freedom in their choices.
Lockbit’s Decline and Recycling Strategy
Once a dominant force, Lockbit’s recent activity has slowed significantly. Now accounting for only 5% of ransomware cases, it’s recycling previously attacked victims to maintain relevance and affiliate confidence. After a major crackdown in February 2024, Lockbit’s once extensive operations have dwindled.
Meow Ransomware’s Data-Driven Extortion
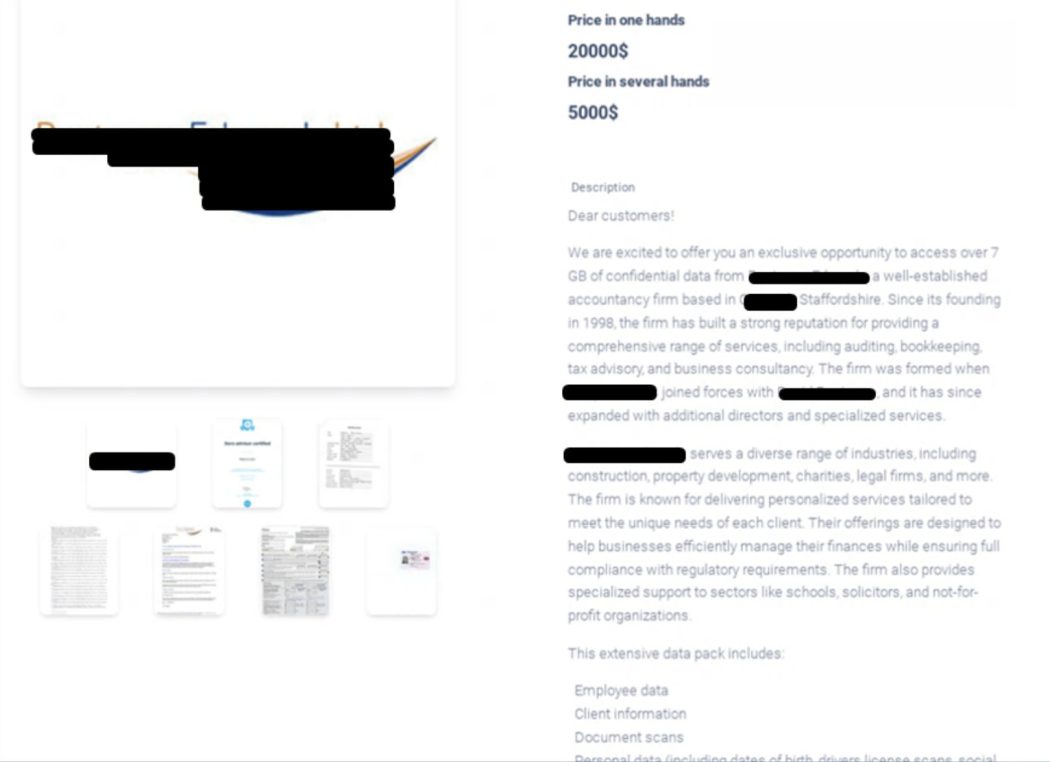
Emerging with a fresh strategy, Meow ransomware has shifted from encryption-based attacks to selling stolen data. Victims must either pay to keep their data private or risk it being sold on the Darkweb, with prices ranging from $500 to $200,000. This approach avoids encryption and thus lowers the attackers’ risk, capitalizing on the high value of personal information.
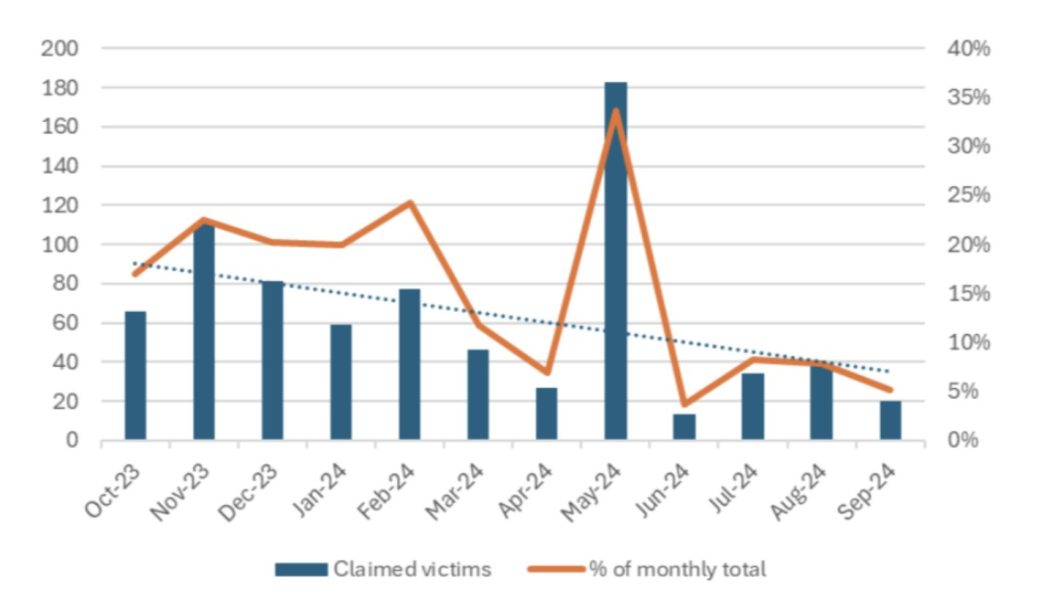
Play Ransomware and Qilin Maintain Steady Activity
Play and Qilin (Agenda) ransomware groups show consistent activity, primarily targeting North American businesses. These groups focus on sectors like manufacturing, showing how ransomware threats vary in intensity but persist across different industries.
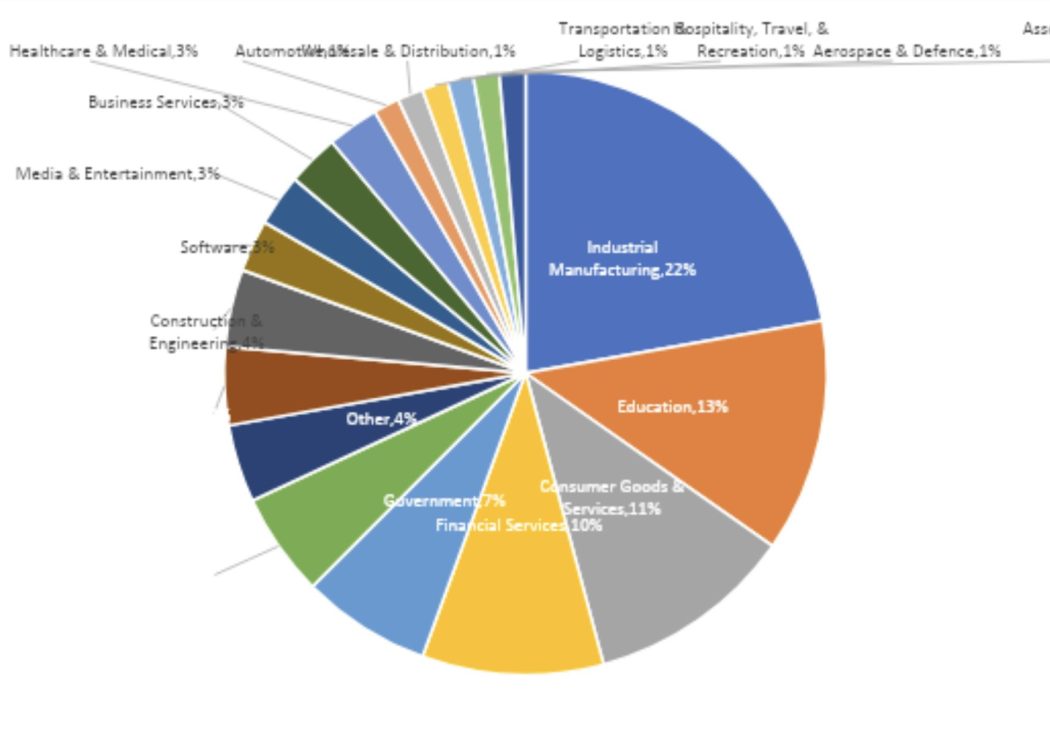
Sector-Specific Threats
Industries like manufacturing, education, and healthcare are ransomware’s top targets, each facing unique challenges:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Legacy systems and a mix of IT and OT networks make manufacturing firms especially vulnerable.
- Education: Schools face a shortage of cyber security resources and have valuable personal data, which is why they’re prime targets.
- Healthcare: Despite public promises to avoid healthcare, ransomware attacks continue, underscoring the sector’s vulnerability and the critical need for operational continuity.
Shifting to Data Extortion
The biggest shift of 2024 is the move toward data extortion. With companies better prepared to recover encrypted data, ransomware groups now focus on stealing and threatening to release sensitive information. This evolution calls for fresh strategies to secure data at every level.
What Enterprises Need to Do
Check Point Research’s findings highlight that AI-driven defenses and zero-trust architectures are now essential. Enterprises must look beyond traditional ransomware solutions and adopt:
- AI-Powered Security: Real-time threat detection and response powered by AI can prevent ransomware attacks before they take hold.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: These provide scalability and continuous protection against ransomware’s evolving tactics.
- Data Encryption and Segmentation: Segmenting networks and encrypting critical data can mitigate the effects of a potential breach.
- Zero-Trust Models: This approach requires every network interaction to be verified, limiting the damage if a breach occurs.
The Future of Ransomware
As ransomware continues to evolve, organizations must stay vigilant. With RaaS models making it easy for less-skilled hackers to launch attacks, and with extortion replacing encryption as the new revenue model, businesses must adopt proactive and adaptive cyber security measures. Zero-trust policies, AI-driven defenses, and sector-specific solutions are essential in facing this rising tide of cyber threats.
Top FAQs
- What is RansomHub and why is it significant?
RansomHub is a new ransomware group that emerged in 2024 and quickly rose to prominence by employing Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) models, allowing affiliates to perform attacks. - Why has Lockbit’s activity declined?
Lockbit has been weakened by recent law enforcement actions and is recycling previous victims to appear active. - What is data extortion, and how does it differ from encryption?
Data extortion involves stealing and threatening to release sensitive data instead of just encrypting it, which is harder for companies to counter. - Why are industrial manufacturing, education, and healthcare frequent targets?
These sectors often have weaker cyber defenses, valuable data, and unique operational challenges that make them attractive to ransomware groups. - What can companies do to protect themselves against ransomware?
Businesses should implement AI-driven security, zero-trust architectures, and strong data encryption to stay protected against evolving ransomware threats.
SEO URL Slug (using new content):
ransomware-threats-2024


