PHILIPPINES – The University of the Philippines (UP) researchers have highlighted the importance of cautious handling and preparation of fresh produce and seafood following the discovery of Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) parasites in local markets. Their findings emphasize the significance of proper cleaning and cooking methods to minimize potential health risks associated with these contaminants.
T. gondii, the culprit behind toxoplasmosis, affects a substantial portion of the global population, especially vulnerable groups like pregnant women and individuals with compromised immune systems. Although many infected individuals remain asymptomatic, severe cases can lead to significant health complications, including inflammation of the brain and vision impairment, particularly in newborns.
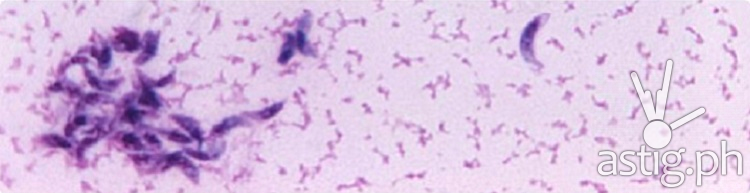
In a study conducted by Cielo Emar M. Paraoan, Ren Mark D. Villanueva, and Marie Christine M. Obusan from UP Diliman’s Institute of Biology, various vegetables and oysters sourced from Central Luzon markets were examined. Among the vegetables tested, including lettuce, cabbage, carrots, cauliflower, and mung bean sprouts, 10% showed traces of T. gondii, with leafy greens exhibiting higher contamination rates compared to root vegetables. Similarly, 9.09% of oyster samples were found to be contaminated, all belonging to the Type I genotype.
While the study sheds light on potential transmission routes of T. gondii through these food sources, the researchers highlighted the need for more extensive studies with larger sample sizes to draw comprehensive conclusions. Additionally, ongoing research is focused on detecting the parasite in environmental samples to further understand its prevalence and transmission dynamics.
The significance of thorough preparation of fresh produce and seafood cannot be overstated, not only for T. gondii but also to mitigate the risks of other parasitic infections. The authors underscored the necessity for better management of biological contaminants and stressed the importance of minimizing T. gondii contamination at its source, particularly in seafood, to reduce health risks associated with consumption.
Their findings, published in the October 2023 issue of the Philippine Journal of Science, serve as a reminder for consumers to adopt proper food safety measures, including washing and cooking practices, when handling market-bought produce and seafood.
For a safe and healthier experience, it’s crucial to adhere to recommended food safety guidelines when preparing fresh produce and seafood, reducing the risks associated with parasites like T. gondii.